MLJ中 线性模型 在回归预测中的简单使用
开始之前
我想向大家介绍一下一些线性模型的用法,以及他们对数据的拟合程度
在我开始学习 MLJ 时,我对他们的拟合能力有所怀疑,经常遇到欠拟合的情况,经过一次简单的测试后,才慢慢了解如何使用模型,处理特征
这里将这个测试介绍给各位
数据准备
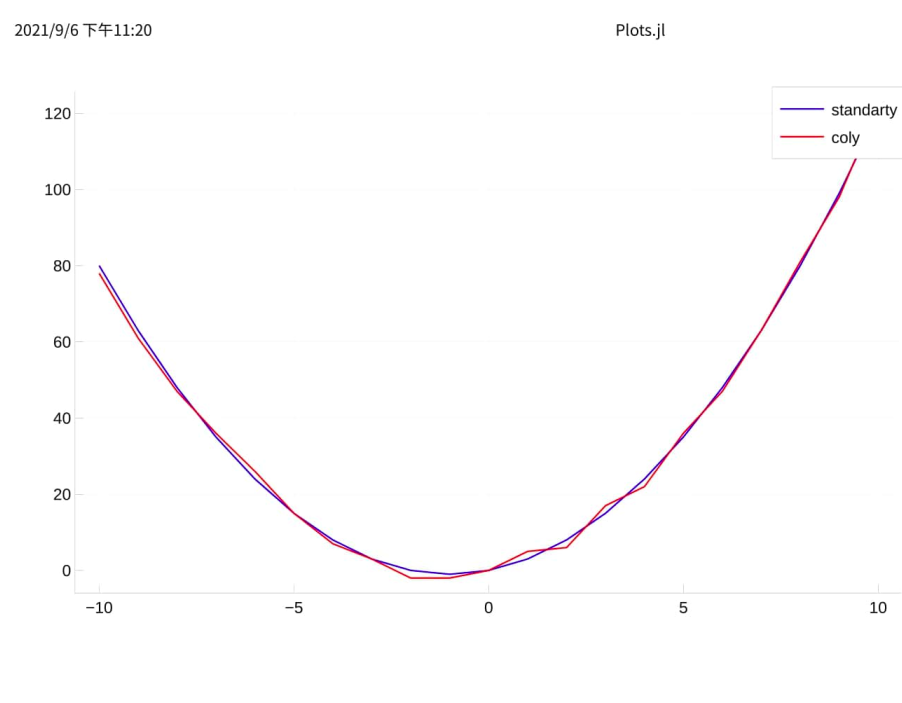
我们模拟对函数 f(x) = x2 + 2x 的拟合,在理想的预测结果 standardy 上加上一点噪音,形成训练用测试结果 coly
接下来依次定义
- f(x)
- standardy
- coly
f(x) = x^2 + 2x colx = DataFrame(x1=-10:10) coly = f.(colx.x1) + rand(-2:2, length(colx.x1)) standardy = f.(colx.x1)
再绘制下图像
plot(colx.x1, standardy, label="standarty", color=:blue) plot!(colx.x1, coly, label="coly", color=:red)
模型介绍
拟合数据我们使用 Ridge 回归,他在损失函数上添加了 L2 正则化
\tag{6}
在 MLJLinearModels 中,RidgeRegressor 为
Ridge regression model with objective function
其中参数有
- lambda (Real): strength of the L2 regularisation.
fit_intercept(Bool): whether to fit the intercept or not.- penalizeintercept (Bool): whether to penalize the intercept.
- solver: type of solver to use (if nothing the default is used). The solver is Cholesky by default but can be Conjugate-Gradient as well. See ?Analytical for more information.
详细介绍以下 fitintercept 和 penalizeintercept ,去 Slack 问了以下,大致可以理解为
fit_intercept在假设函数上是否添加 偏差(bias)penalize_intercept是否惩罚偏差,修改其数值
接下来模型训练,直接调优得到最优模型,得到输出结果
using MLJLinearModels, StableRNGs rng = StableRNG(1234) ridge = RidgeRegressor() r_lambda = range(ridge, :lambda, lower = 0.01, upper = 10, scale=:linear) tuning = Grid(resolution = 20, rng=rng) resampling = CV(nfolds = 6, rng=rng) self_tuning_model = TunedModel(model = ridge, range = r_lambda, tuning = tuning, resampling = resampling, measure = rms ) self_tuning_mach = machine(self_tuning_model, colx, coly) fit!(self_tuning_mach) best_model = fitted_params(self_tuning_mach).best_model best_mach = machine(best_model, colx, coly) fit!(best_mach) outputy = predict(best_mach, colx)
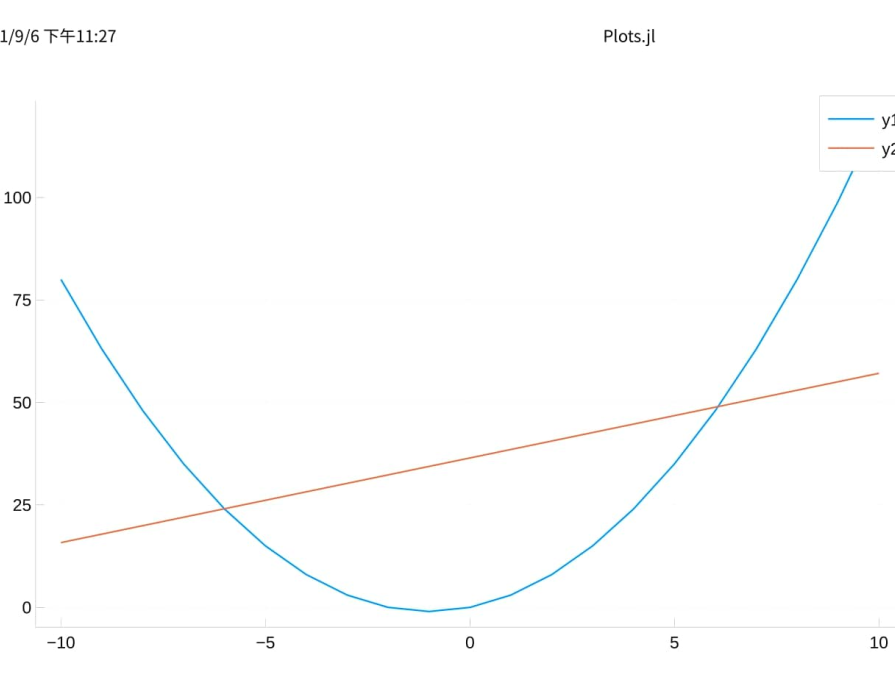
然后我们通过图像查看拟合程度
plot(colx.x1, standardy, label="standardy", color=:blue) plot!(colx.x1, outputy, label="outputy", color=:red)
可以看到,欠拟合了
添加特征
应对欠拟合的情况我们可以通过添加特征来解决
回到上面的问题,由于 f(x) = x2 + 2x ,提供的数据中只有 x1=x 一个特征,我们尝试再添加一个特征 x2=x2
let g(x) = x^2 colx.x2 = g.(colx.x1) self_tuning_machine = machine(self_tuning_model, colx, coly) fit!(self_tuning_machine) best_model = fitted_params(self_tuning_mach).best_model best_mach = machine(best_model, colx, coly) fit!(best_mach) outputy = predict(best_mach, colx) plot(colx.x1, standardy, label="standardy", color=:blue) plot!(colx.x1, outputy, label="output", color=:red) |> display end
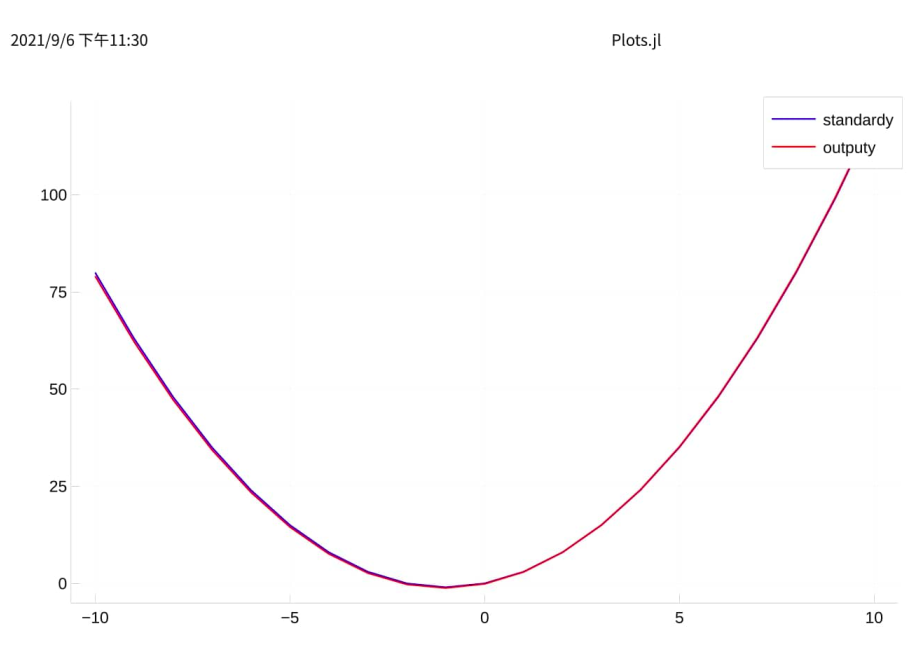
可以看到,挺完美
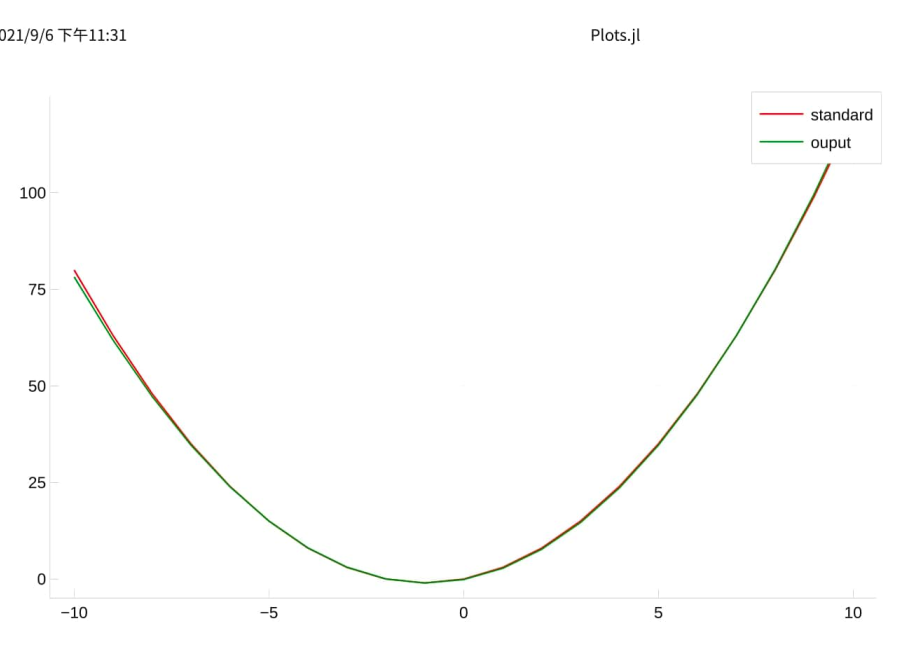
那我们再添加一个特征 x3=x3
let g(x) = x^3 colx.x3 = g.(colx.x1) self_tuning_machine = machine(self_tuning_model, colx, coly) fit!(self_tuning_machine) best_model = fitted_params(self_tuning_mach).best_model best_mach = machine(best_model, colx, coly) fit!(best_mach) outputy = predict(best_mach, colx) plot(colx.x1, standardy, color=:blue, label="standard") plot!(colx.x1, outputY, color=:red, label="ouputy") |> display end
最后说明
这次测试没有使用训练集和测试集,相当简陋,只是作为实验